Least Common Ancestor Java Program
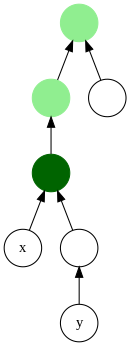
In this tree, the lowest common ancestor of the nodes x and y is marked in dark green. Other common ancestors are shown in light green.
This is the java program to find the least common ancestor in a binary search tree,user can insert,traverse and find common ancestor in the binary search tree.
In graph theory and computer science, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes v and w in a tree or directed acyclic graph (DAG) is the lowest (i.e. deepest) node that has both v and w as descendants, where we define each node to be a descendant of itself (so if v has a direct connection from w, w is the lowest common ancestor).
The LCA of v and w in T is the shared ancestor of v and w that is located farthest from the root. Computation of lowest common ancestors may be useful, for instance, as part of a procedure for determining the distance between pairs of nodes in a tree: the distance from v to w can be computed as the distance from the root to v, plus the distance from the root to w, minus twice the distance from the root to their lowest common ancestor (Djidjev, Pantziou & Zaroliagis 1991). In ontologies, the lowest common ancestor is also known as the least common subsumer.
In a tree data structure where each node points to its parent, the lowest common ancestor can be easily determined by finding the first intersection of the paths from v and w to the root. In general, the computational time required for this algorithm is O(h) where h is the height of the tree (length of longest path from a leaf to the root). However, there exist several algorithms for processing trees so that lowest common ancestors may be found more quickly. Tarjan’s off-line lowest common ancestors algorithm, for example, preprocesses a tree in linear time to provide constant-time LCA queries. In general DAGs, similar algorithms exist, but with super-linear complexity.
import java.io.*;
class node
{
int data;
node lchild,rchild;
}
class BST {
public static node root=null;
public static int flag=0;
int dec;
node temp=null,newnode=null,prev=null;
public void insert(int num)
{
temp=root;
newnode=new node();
newnode.data=num;
newnode.lchild=null;
newnode.rchild=null;
while(temp!=null)
{
if(num<temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.lchild;dec=0;}
else if(num>temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.rchild;dec=1;}
else if(num==temp.data){System.out.println("Already Exists n"); return;}
}
if(flag==0){root=newnode;flag=1;}
if(dec==0){try{prev.lchild=newnode;}catch(Exception e){}}
else if(dec==1){prev.rchild=newnode;}
}
public void inorder(node jp)
{
if(jp!=null){
inorder(jp.lchild);
System.out.println(" "+jp.data);
inorder(jp.rchild);
}
}
public void preorder(node jp)
{
if(jp!=null){
System.out.println(" "+jp.data);
preorder(jp.lchild);
preorder(jp.rchild);
}
}
public void postorder(node jp)
{
if(jp!=null){
postorder(jp.lchild);
postorder(jp.rchild);
System.out.println(" "+jp.data);
}
}
public void cas(int node1,int node2)
{
int[] arr1=new int[20];
int[] arr2=new int[20];
int len1=0,len2=0,i=0,j=0;
temp=root;
while(temp!=null)
{
arr1[i]=temp.data;i++;
if(node1<temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.lchild;dec=0;}
else if(node1>temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.rchild;dec=1;}
else if(node1==temp.data){break;}
}
temp=root;
prev=null;
while(temp!=null)
{
arr2[j]=temp.data;j++;len2++;
if(node2<temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.lchild;dec=0;}
else if(node2>temp.data){prev=temp;temp=temp.rchild;dec=1;}
else if(node2==temp.data){break;}
}
System.out.println("Path Length1 "+len1);
System.out.println("Path Length2 "+len2);
for(int m=0;m<=len1;m++)
{
System.out.println(" "+arr1[m]);
}
for(int n=0;n<=len2;n++)
{
System.out.println(" "+arr2[n]);
}
int flen,cas=0,k=0,l=0;
if(len1<len2){ flen=len2;}
else {flen=len1;}
for(;k<flen;k++)
{
for(;l<flen;l++)
{
if(arr1[k]==arr2[l])
{
System.out.println("Entered "+arr1[k]);
cas=arr1[k];
}
}
}
if(cas==0)
System.out.println("Common Ancestor "+root.data);
else
System.out.println("Common Ancestor "+cas);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ch=0,ele=0,node1=0,node2=0;
BST b=new BST();
System.out.println("Enter the Choicen 1.INSERT n 2.INORDER n 3.PREORDER n 4.POSTORDER n 5.Common Ancestor n 6.Exitn");
DataInputStream in=new DataInputStream((System.in));
try{
ch=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
}
catch(Exception e){}
while(ch<6)
{
switch(ch)
{
case 1: System.out.println("Enter the Element to be Insertedn");
try{
ele=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
}
catch(Exception e){}
b.insert(ele);
break;
case 2: b.inorder(b.root); break;
case 3: b.preorder(b.root); break;
case 4: b.postorder(b.root); break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Enter Node1 and Node2n");
try{
node1=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
node2=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
}
catch(Exception e){}
b.cas(node1, node2);
break;
}
System.out.println("nEnter the Choicen");
try{ch=Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
}
}

Recent Comments